To provide services at the highest level, we use cookies. Using the website requires you to choose settings related to their storage on your device. If you want to know what each type of cookie is used for, click the Details button below.
Sarcoidosis – causes, effects, treatment18 lutego 2022 |
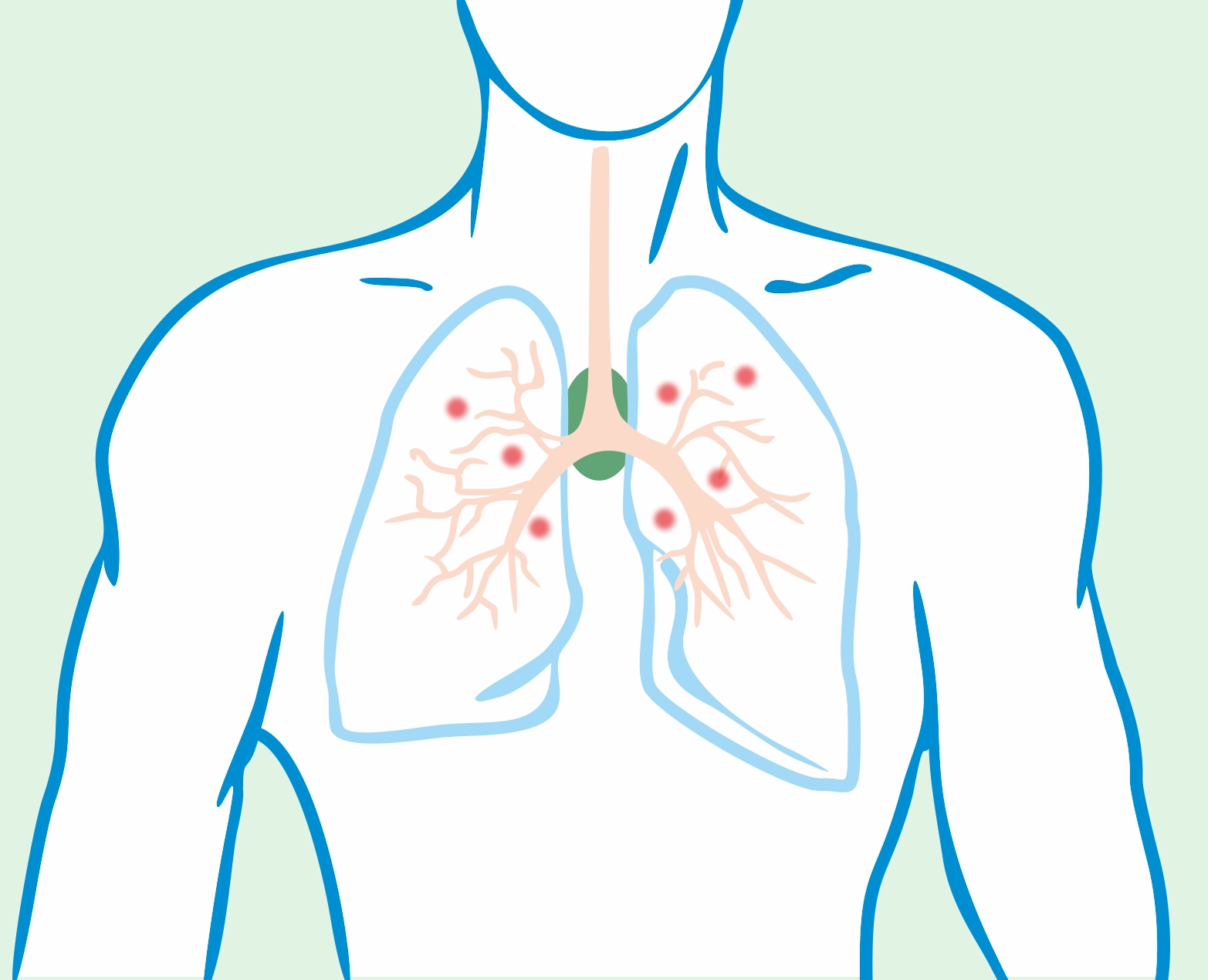
Sarcoidosis is a rare disease characterized by the formation of small clusters of inflammatory cells called sarcoid granulomas in various organs of the body. Most commonly, sarcoidosis affects the lungs, but it can also impact other areas such as the skin, eyes, heart, or digestive organs.
Symptoms of sarcoidosis are diverse and depend on the affected area. They often include fatigue, shortness of breath, cough, joint pain, and skin changes. In some cases, sarcoidosis may be asymptomatic. It's important to pay close attention to potential signs.
Sarcoidosis can be mild and resolve on its own, but in some cases, it can lead to serious complications such as lung scarring, organ failure, or eye damage. Therefore, monitoring and treatment are crucial in managing sarcoidosis.
The prognosis for living with sarcoidosis varies and depends on factors such as the progression of the disease, its location, and the effectiveness of treatment. Many patients lead normal lives, but in some cases, more intensive treatment and regular monitoring may be necessary. Only about 1% of sarcoidosis patients die from the disease.
Sarcoidosis is managed by various specialists depending on symptoms and affected organs. Often, a pulmonologist plays a crucial role as sarcoidosis most commonly affects the lungs. However, rheumatologists, dermatologists, cardiologists, or ophthalmologists may also be involved in treatment, depending on the patient's needs. Comprehensive care for individuals with sarcoidosis is ensured through collaboration with a team of specialists within a consortium.