To provide services at the highest level, we use cookies. Using the website requires you to choose settings related to their storage on your device. If you want to know what each type of cookie is used for, click the Details button below.
Disk sequestration – causes, effects, treatment 5 czerwca 2024 |
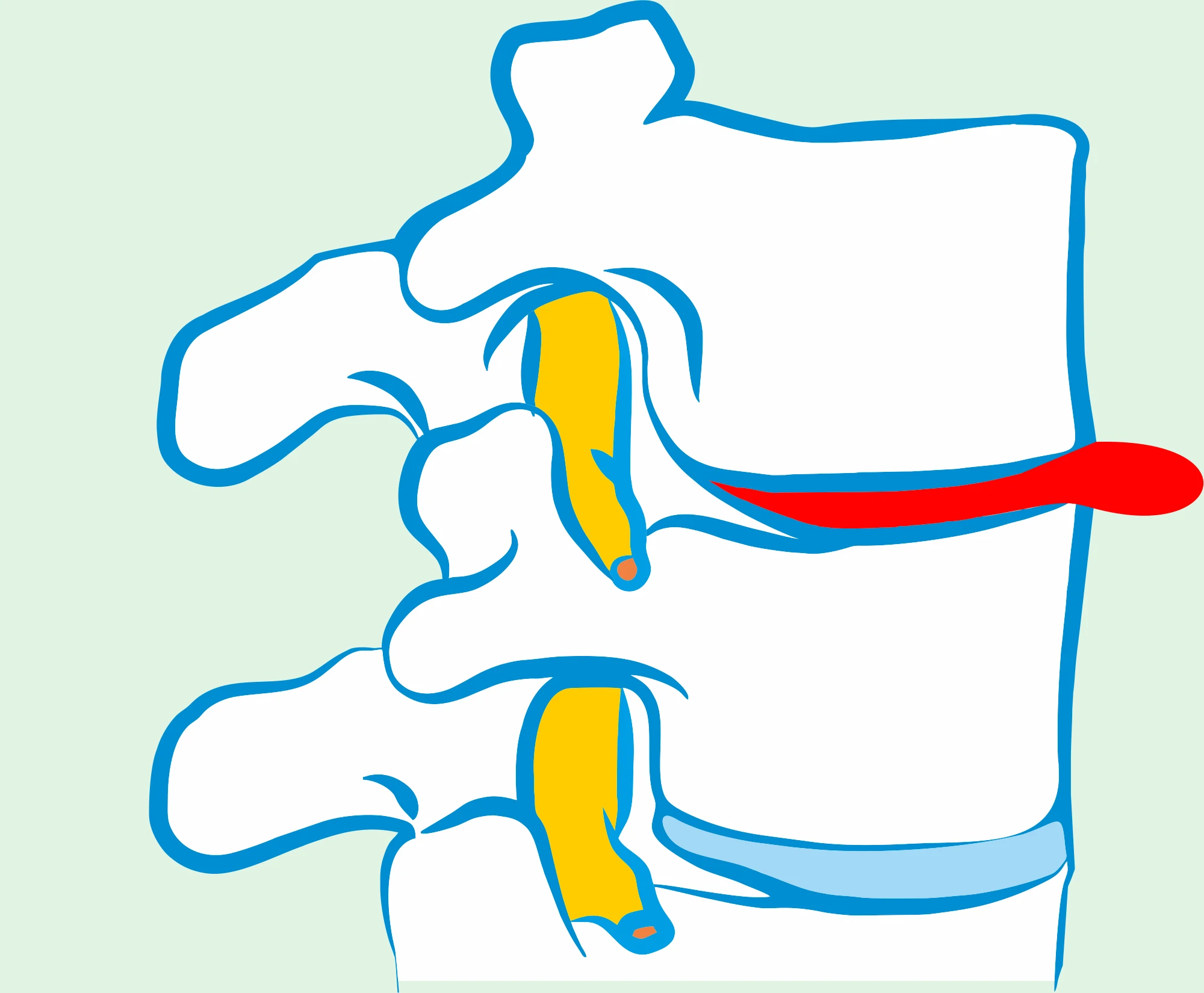
Disc sequestration is an advanced stage of disc disease where a fragment of the nucleus pulposus moves beyond the annulus fibrosus of the intervertebral disc, compressing nearby nerve structures and consequently causing intense pain.
The most common causes of disc sequestration are mechanical injuries, spinal overloads, prolonged sitting, and degenerative processes associated with aging. Risk factors predisposing to disc sequestration include poor posture, low physical activity, and abdominal obesity.
Symptoms of disc sequestration include sharp pain radiating to the limbs, muscle weakness, numbness, sensory disturbances, and in extreme cases, serious neurological damage such as loss of bladder or bowel control.
Treatment for disc sequestration includes conservative methods such as painkillers, physical therapy, and spinal exercises. In advanced cases, surgical intervention may be necessary, such as microdiscectomy.
Pain associated with disc sequestration can make it difficult to fall asleep and cause frequent awakenings, leading to sleep deprivation. It is important to manage pain, use ergonomic pillows and mattresses, and practice relaxation techniques.
| Thank you for adding a comment! |