To provide services at the highest level, we use cookies. Using the website requires you to choose settings related to their storage on your device. If you want to know what each type of cookie is used for, click the Details button below.
Is it possible to buy a mattress for years? 5 stycznia 2024 |
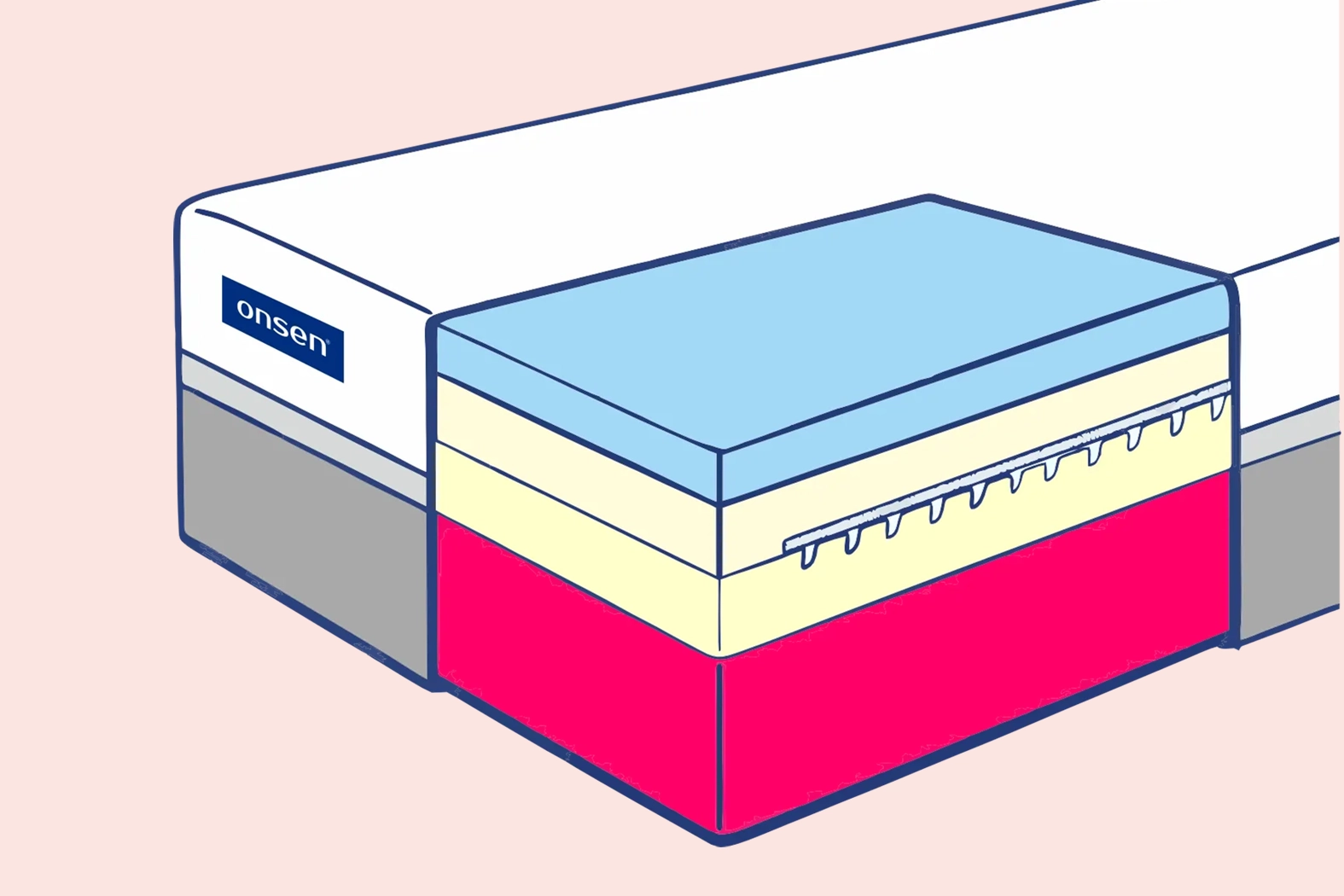
Yes, the foam parameter is a crucial criterion for evaluating the durability of a mattress. It consists of a letter designation (V, T, or HR) and a four-digit or five-digit sequence, where the first two digits represent density, and the subsequent ones represent firmness. This letter designation is key because it indicates the type of foam. The higher the density of the foam, the more durable it will be, and consequently, the mattress will last longer.
HR foams are characterized by an open cell structure, allowing air circulation and the foam's return to its original shape. They also positively impact the dynamics of the mattress. Meanwhile, T foams have closed cells that are less durable due to cracking, leading to a quick sinking of the mattress.
Although latex often comes from a natural source, such as rubber milk, its production typically involves harmful chemical substances. It turns out that more durable and less harmful mattresses are often made from synthetic latex. The more natural latex in the mattress, the greater the risk of it breaking, thus reducing its durability.
Latex does not allow air to pass through due to its structure. Vertical holes in latex mattresses are considered ineffective because warm air does not flow downward but upward. The structure of latex often prevents natural air circulation, affecting sleep comfort and reducing its lifespan.
The durability of a mattress is usually determined by several key factors that are worth considering when choosing a product. At the forefront is the type of foams used, which is crucial. Mattresses based on high-resilience HR foams are characterized by the greatest durability due to their open cell structure, allowing efficient air circulation. Another important aspect is the density of the foams, where higher density typically translates to a longer mattress lifespan. Additionally, the construction of the mattress plays a significant role.