To provide services at the highest level, we use cookies. Using the website requires you to choose settings related to their storage on your device. If you want to know what each type of cookie is used for, click the Details button below.
How not to be defeated by tendinopathy?24 marca 2022 |
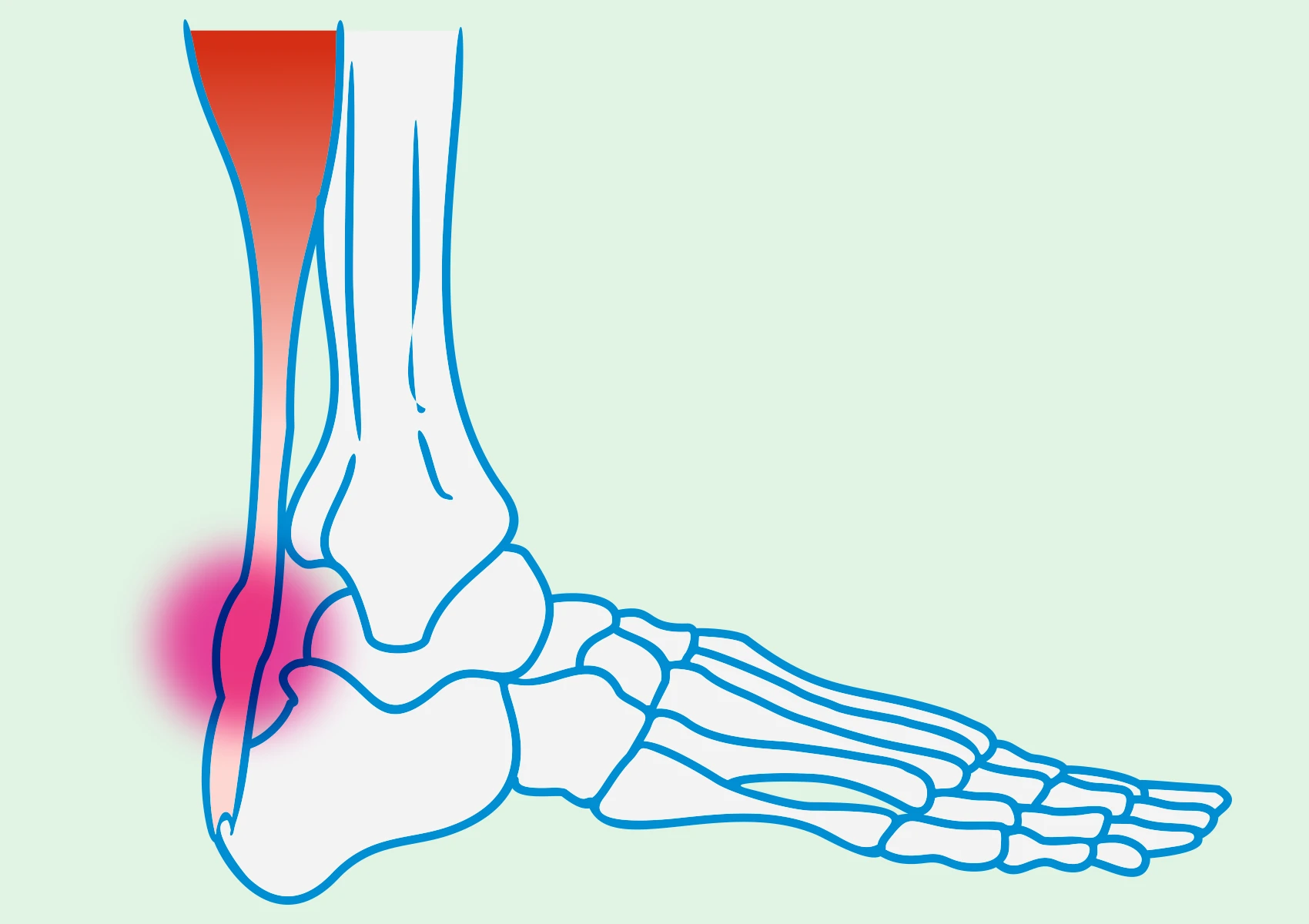
Tendinopathy is a general medical term that describes various pathological conditions of tendons. It is characterized by significant changes in the structure of tendons, degeneration, or damage to these structures. This condition can affect tendons in different areas of the body, leading to pain, restricted movement, and loss of function.
Rotator cuff tendinopathy is a specific type of tendinopathy characterized by the deposition of calcium salts in the tendons of the rotator cuff muscles, located in the shoulder area. This process increases pressure in the tendon and reduces the space for surrounding tissues. It is also referred to as calcific tendinitis of the rotator cuff. It can result in pain, limited range of motion, and loss of shoulder function.
Shoulder tendinopathy is a general term covering all pathological conditions of tendons in the shoulder area. It primarily affects the muscles of the rotator cuff, such as the supraspinatus, infraspinatus, subscapularis, and teres minor. This condition may result from overuse, injury, or degeneration.
The treatment of tendinopathy is typically managed by various specialists, depending on the severity of the condition. The treatment plan usually involves orthopedic specialists, physiotherapists, and psychologists. Sometimes, rheumatologists and neurologists may also be involved. Consulting with a specialist allows for tailoring the therapy to the individual needs of the patient.
The treatment of tendinopathy depends on the severity of the condition and its underlying causes. In the early stages of tendinopathy, activity restriction, thermal therapy, and physiotherapy aimed at strengthening and stretching tendons are often recommended. It is also important to prioritize sleep hygiene. Symptomatic relief may involve pain relievers or corticosteroids. In more severe cases, consideration may be given to corticosteroid injections or even surgical intervention, especially if other methods do not yield results.