To provide services at the highest level, we use cookies. Using the website requires you to choose settings related to their storage on your device. If you want to know what each type of cookie is used for, click the Details button below.
What does Lasègue's sign indicate?20 sierpnia 2023 |
Differences between the Lasègue's sign and other back pain symptoms arise from the characteristic and mechanism of occurrence of this specific symptom. The Lasègue's sign, also known as the straight leg raising sign, stands out as an indicator of compression or irritation of the sciatic nerve.
In contrast to musculoskeletal pain, the Lasègue's sign is radiating pain that increases during the raising of the elevated leg, especially in a lying position. This sign also differentiates itself from chronic back pain that results from long-term structural issues of the spine. Furthermore, the Lasègue's sign is useful in identifying these conditions as it may indicate compression of the sciatic nerve.
In cases of back pain related to injuries such as various falls or accidents, the Lasègue's sign also stands out. It is closely correlated with the compression of the sciatic nerve, which is typical in herniated disc or radiculopathy. Localized pain associated with a specific spinal area or muscles also differs from the Lasègue's sign. The latter triggers radiating pain along the sciatic nerve, which can extend to the buttock, thigh, and even foot.
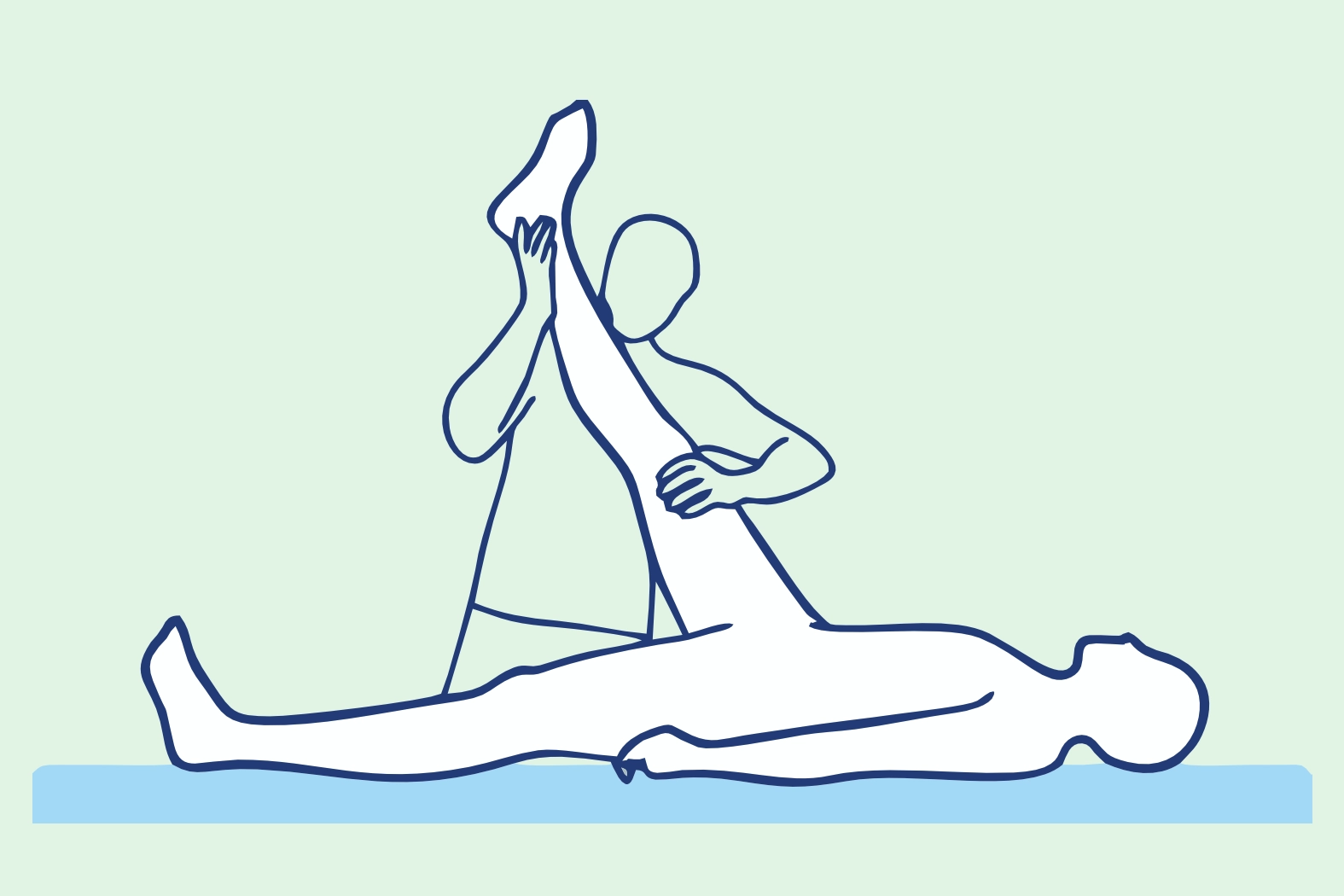
The Lasegue's sign, also known as the straight leg raise test, is a clinical test used to diagnose issues with the sciatic nerve and the spine. It involves inducing radiating pain along the sciatic nerve by raising the extended lower limb.
A positive Lasegue's sign, meaning the occurrence of pain or radiating discomfort during the test, can suggest compression of the sciatic nerve. This could be caused by problems such as a herniated disc, spinal stenosis, or root syndromes.
The Lasegue's test involves lifting the patient's extended leg while they are in a lying position. The doctor raises the patient's leg until the patient reports pain or discomfort along the sciatic nerve. The angle at which the pain occurs might be significant for diagnosis.
The crossed femoral Lasegue's sign, also known as the reverse Lasegue's sign, is a test used to diagnose issues with the spinal nerves. It involves lifting the healthy leg of the patient on the opposite side. If pain occurs on the side where the symptom wouldn't appear in the standard test, it could indicate compression of a nerve root.
Both of these clinical features are used to diagnose neurological problems but in different contexts. The Lasegue's sign involves inducing pain along the sciatic nerve by raising the extended leg. On the other hand, the Kernig's sign is a symptom seen in cases of meningeal infections, where lifting the extended leg of the patient causes resistance or pain in the lower back.