To provide services at the highest level, we use cookies. Using the website requires you to choose settings related to their storage on your device. If you want to know what each type of cookie is used for, click the Details button below.
How to reduce tension in the quadratus lumborum muscle?15 lutego 2024 |
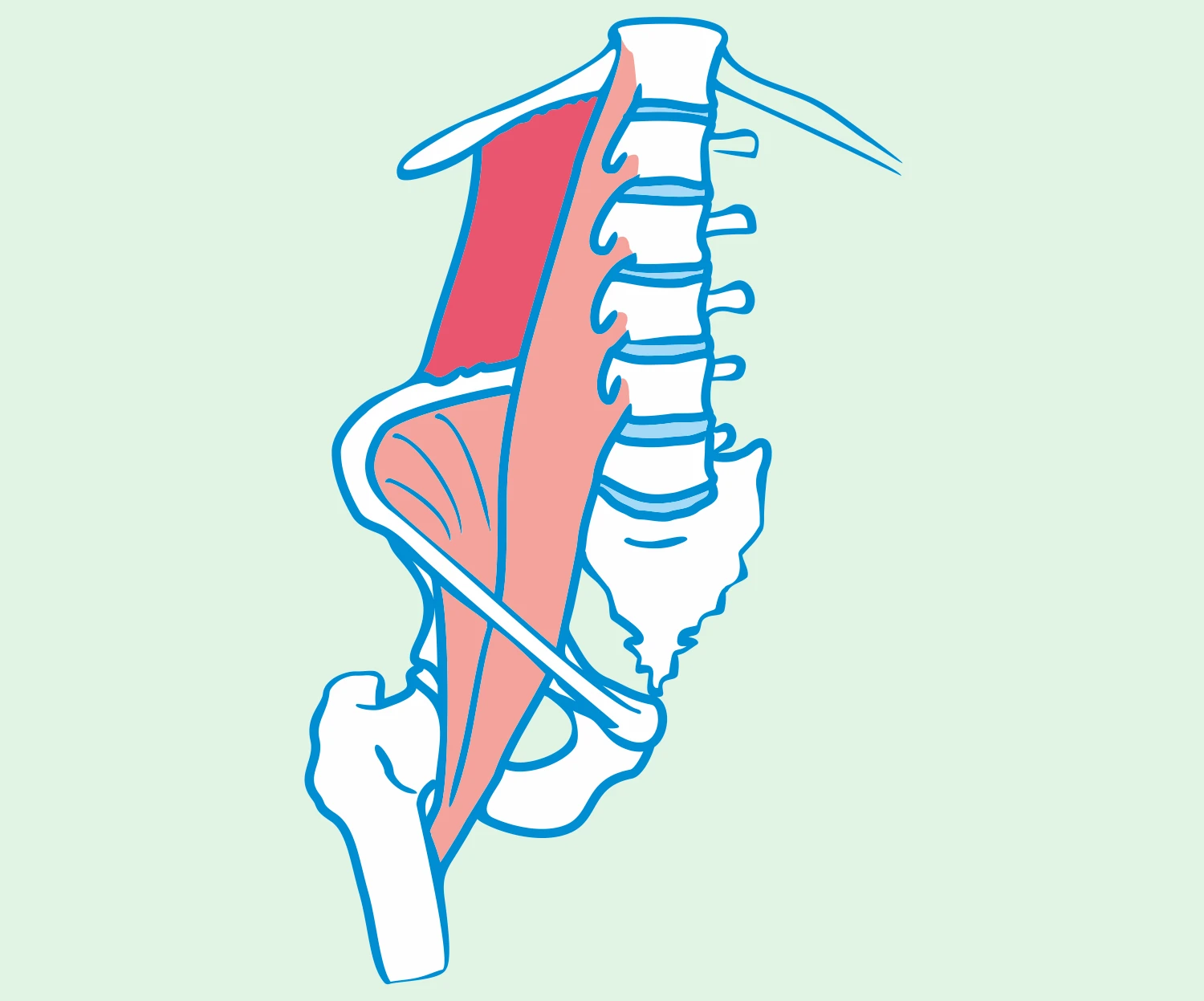 |
The quadratus lumborum muscle, also known as the QL muscle, is an important anatomical structure in the lower back. It is a back muscle that extends from the lower spine to the bottom of the ribcage. Its main functions include stabilizing the lumbar spine and participating in torso rotation movements.
To strengthen the quadratus lumborum muscle, it is essential to perform appropriate strengthening exercises. QL muscle exercises include spinal stabilization, core muscle strengthening, and postural restoration techniques. It is important to perform exercises under the guidance of a specialist and always adjust their intensity to your level of physical fitness.
Pain in the quadratus lumborum muscle can result from various causes, including poor postural alignment, overuse, injury, or even improper exercise execution. Excessive strain on the quadratus lumborum muscle leads to muscle imbalance in the back area and posture issues, which can contribute to discomfort or pain in that region.
The quadratus lumborum muscle is located in the lower back, at the level of the lumbar spine. It is the area between the lower spine and the bottom edge of the shoulder blade. Comprising four parts, it has a distinctive shape. It is vascularized by the subcostal artery, lumbar arteries, and iliolumbar artery. Its innervation is provided by the twelfth thoracic intercostal nerve and branches of the lumbar plexus (TH12 and L1-3).
Postural Restoration Technique (PRI) is a therapeutic approach that focuses on restoring balance between the left and right sides of the body and improving posture. This method utilizes strengthening exercises, breathing techniques, and body positioning to minimize postural imbalances and enhance muscle function. PRI is often applied in physical therapy and functional training to reduce pain, improve mobility, and restore optimal body posture.